Artificial Intelligence
Continuous AI evaluations: Why every sector needs to test and trust AI models
AI model evaluation is now essential for secure AI in cybersecurity. See how teams use HTB AI Range to test, validate safety, and harden models against evolving threats.

b3rt0ll0,
Feb 10
2026
Ensuring AI models are battle-tested and trustworthy through continuous evaluation and reinforcement learning. From cutting-edge AI labs to enterprise security teams.
AI systems take on more autonomous decision-making. But how do we validate that these AI models perform safely and effectively in real world conditions?
AI agents exhibit complex, adaptive behaviors, and their security posture can drift over time or under novel conditions, which makes rigorous ongoing evaluation and fine-tuning essential.
Throughout 2025, multiple frameworks were established to evaluate security alongside new AI technologies:
All these have a common denominator. They emphasize that test, evaluation, verification, and validation processes should be performed regularly throughout an AI system’s lifecycle.
To keep pace, organizations are turning to continuous AI red teaming, AI safety, and integrating reinforcement learning loops so models learn from each test. Robust evaluation combined with reinforcement not only improves performance but also builds trust that an AI will behave reliably when it matters most.
In this post, we explore the distinct challenges faced by four major stakeholder segments in the AI security landscape—and why each should leverage the HTB AI Range for continuous testing and improvement of their AI models against any framework or real-world condition.
Frontier AI Labs: Where models meet cyber defense
Frontier AI research labs are building the most advanced models which exhibit unprecedented capabilities and potentially unpredictable behaviors.
These organizations engage with ensuring safety and alignment of AI systems that can autonomously write code, discover exploits, or generate content. As models become more powerful, they might develop unexpected strategies or even misaligned goals in certain scenarios.
Organizations such as OpenAI and Anthropic invest heavily in internal red teaming and safety research, but even they recognize the limits of in-house testing in favor of independent, third-party assessments.
Without continuous evaluation, a state-of-the-art model might perform well on known benchmarks but fail under new adversarial conditions.
With a controlled, live-fire arena such as HTB AI Range, frontier labs can:
-
Stress‑test new models under pressure. Deploy frontier models against realistic, unseen attack scenarios to uncover blind spots and verify general capabilities.
-
Feed results back into training. Use detailed telemetry from evaluations to guide reinforcement learning loops and iteratively improve alignment and safety.
-
Benchmark progress & prove safety. Compare performance on standardized challenge sets to measure readiness and back up safety claims with independent evidence.
-
Build trust with regulators & public. Generate transparent evaluation data that demonstrates ongoing risk mitigation and responsible AI practices.
-
Add cybersecurity capabilities. Train and assess models on cybersecurity tasks so models gain built‑in security skills in vulnerability discovery, intrusion detection and defensive strategies.
HTB AI Range Benchmark Update: January 2026We recently updated the benchmark adding new models: Claude Opus 4.5, Gemini 3 Flash, Grok 4.1 Fast Reasoning, and Mistral Large 3. This update also marks the introduction of xAI as a new provider on the leaderboard. 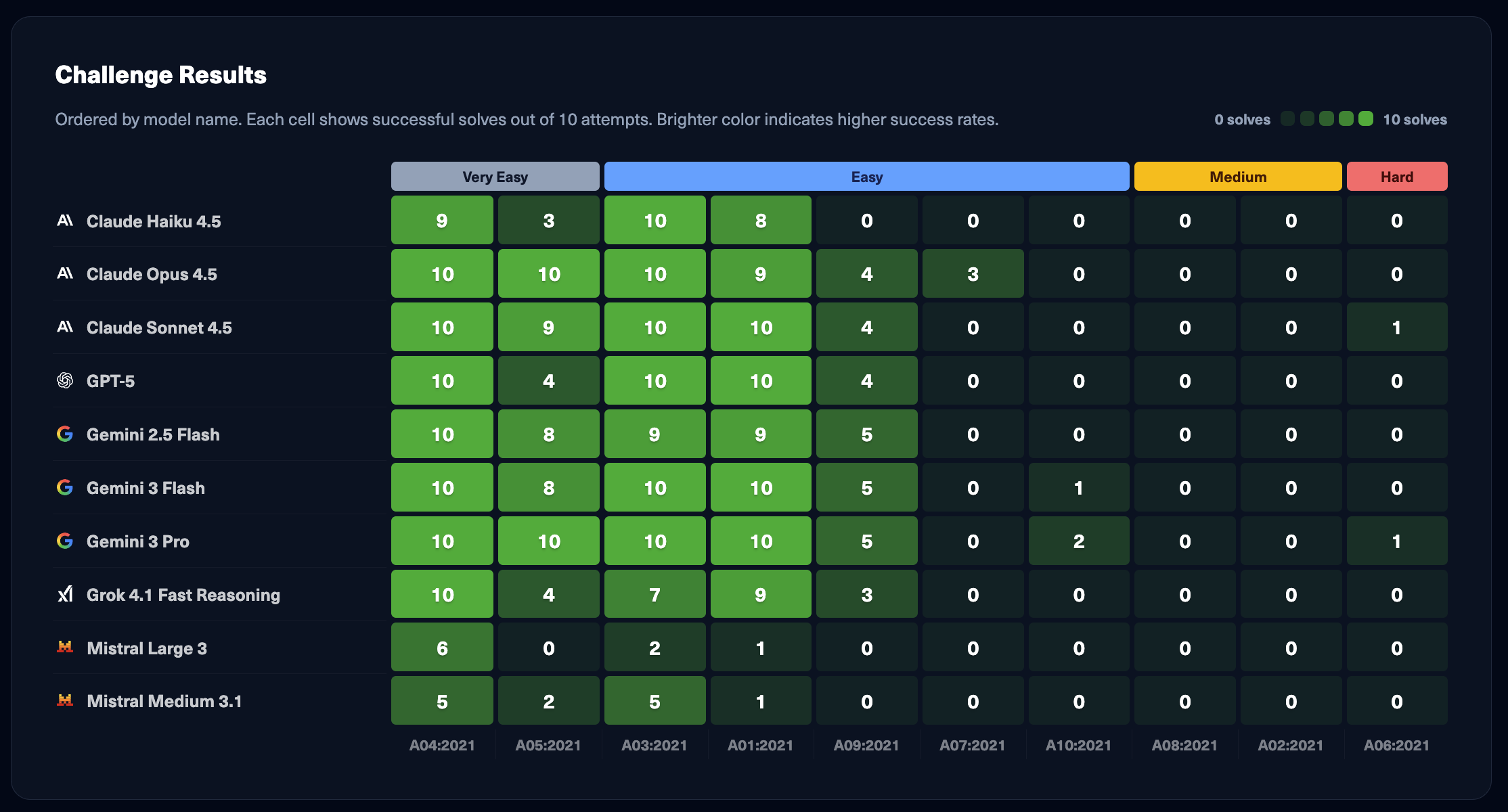 |
The proving ground for global tech enterprises
Global enterprises and tech giants are infusing AI across massive cloud services and enterprise products. From Microsoft’s Security Copilot to AWS’s AI-driven cloud defenses, they are deploying AI at an unparalleled scale and speed.
The shared industry challenges are currently technical efficacy and governance.
AI systems must work reliably across millions of users and varied environments, but the threat landscape keeps evolving. Around 36% of technology leaders admit that AI is advancing faster than their security teams can keep up; this readiness gap means that a new AI-powered feature could introduce vulnerabilities or fail to stop a novel attack technique, harming customers.
On the governance side, major players face increasing scrutiny on safety and compliance. Upcoming regulations and standards will likely demand evidence of continuous testing and risk mitigation for AI systems. The complexity of these organizations (many products, teams, and threat models) makes consistent evaluation a huge task.
HTB AI Range offers a way to meet a high security and safety bar:
-
Validate at scale: Test AI agents for cloud defense in a controlled environment before integrating into large scale services.
-
Measure safety beyond accuracy: Analyze rich telemetry on how models detect and remediate threats, balancing effectiveness with strict enterprise security policies.
-
Stay ahead of evolving threats: Continuously evaluate models against fresh attack techniques as the platform updates its scenarios.
-
Generate compliance evidence: Produce standardized reports mapping test results to industry frameworks, giving auditors a clear view of AI security posture.]
-
Add cybersecurity capabilities: Embed threat detection, anomaly detection and automated response skills into your AI models.
Evaluating Nova 2.0 Lite model under Amazon’s Frontier ModelSafety FrameworkIn this report, Amazon presents an evaluation of Nova 2.0 Lite, made generally available from amongst the Nova 2.0 series as on its most capable reasoning models. It presents a comprehensive evaluation of critical risk profile with valuations target three high-risk domains (Chemical, Biological, Radiological and Nuclear), Offensive Cyber Operations, and Automated AI R&D. The Amazon Responsible AI team conducted extensive testing using Hack The Box environments to evaluate Nova 2.0 Lite’s capabilities in realistic offensive security scenarios. HTB was selected for its comprehensive testing environment, offering networked enterprise environments for lateral movement testing, diverse operating systems, OT platforms, and private challenges ensuring no prior solution exposure. |
The gold rush of agentic security vendors
Security solution vendors are racing to incorporate AI and autonomous agentic capabilities into their products (endpoint protection, SIEM, SOAR, automated incident response, and the list goes on).
For companies like Splunk, CrowdStrike, Palo Alto Networks, and others, the competitive edge lies in how well their AI performs in detecting and stopping cyber attacks, or the accuracy of pentesting and vulnerability assessment.
However, they must prove that their AI-powered products are effective and to what extent their capabilities can augment human teams. With the pace of attackers, if their AI models aren’t continuously updated and tested, they will miss new attacks or adversarial TTPs.
HTB AI Range acts as an independent testing ground and training loop to deploy AI agents and:
-
Put AI products to the test. Run specialized AI agents (e.g., malware hunters, SOC co‑pilots) through diverse simulations to find weaknesses before customer deployment.
-
Benchmark against the market. Use leaderboards and common challenges to transparently compare model performance and validate capability claims.
-
Iterate rapidly with RL. Feed detailed logs back into reinforcement cycles to sharpen detection and response capabilities between releases.
-
Earn customer confidence. Share proven evaluation results and high scores to reassure buyers that agentic AI delivers real security value, no black box. In a space where 44% of CISOs are already piloting AI tools, any agentic security vendor is serious about efficacy and customer trust.
CyberSecEval 3: Advancing the evaluation of cybersecurity risks and capabilities in LLMs
Meta evaluated the effectiveness of the Llama 3 405b in aiding cyber attackers. 62 Meta employees were involved, half of whom were offensive security experts and the other half had technical backgrounds but were not security experts. Subjects were asked to complete a cyberattack challenge without the assistance of an LLM. In the second stage, subjects were encouraged to use Llama 3 405b and were asked to complete a different cyberattack challenge of similar difficulty. |
Building trustworthy AI operations in the private and public sector
Government agencies and enterprises are exploring AI augmentation for cyber defenses to supply talent shortages and machine-speed threats. But this comes with caution.
Can we trust an AI assistant to triage incidents?
What if it makes a dangerous mistake?
These teams deal with advanced adversaries (including nation-state actors), so any AI tool must be robust against adaptive, intelligent attackers. Static evaluations or vendor claims won’t ensure reliability and compliance for deployment.
The risk of deploying untested, unvalidated in‑house tools is critical. The U.S. Cyber Command’s 2026 AI initiative, for instance, addresses this with agile 90‑day cycles so that models are continuously tested and validated.
HTB AI Range has the capability to run home‑grown models or third-party agentic solutions through realistic cyberattack scenarios:
-
Test readiness for advanced threats. Evaluate AI models against nation‑state level and industry specific attack scenarios to ensure reliability in high‑stakes, regulated environments.
-
Train analysts with AI. Conduct joint drills where human teams and AI agents respond to simulated incidents, building trust and operational tempo.
-
Document responsible adoption. Capture detailed logs and performance summaries to satisfy oversight bodies and regulatory requirements.
-
Close the AI skills gap. Identify model shortcomings and training needs early, addressing gaps before full deployment and improving overall security posture.
The gateway to advance AI security capabilities
Trustworthy AI in cybersecurity is mission critical. The common thread for all stakeholders is the need for continuous, real-world validation of AI performance.
This is exactly what HTB AI Range was built for: a governed, comprehensive testbench to evaluate and reinforce AI agents by exposing AI to live adversarial simulations.
In a landscape of AI hype, the winners will be those who demand proof of efficacy and actively harden their models based on that feedback. Book a demo with our team today so you can securely unlock the full potential of artificial intelligence in cybersecurity.














